What Is Structured Data and How It Works
Table of Contents
What Is Structured Data?
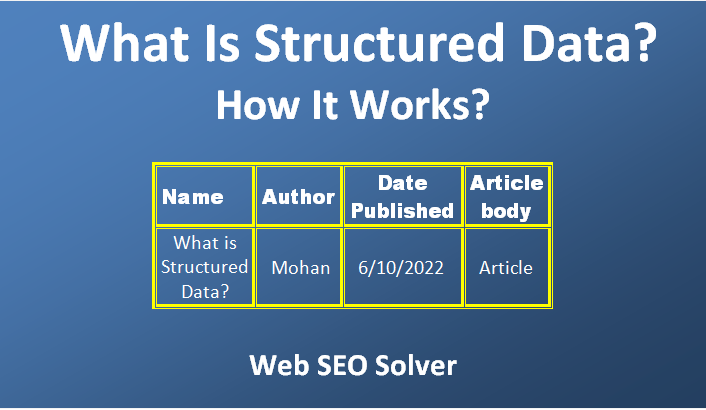
Data that are kept in a structure such as a table to access them efficiently can be called structured data.
Here the table is a container of data that is made up of columns and rows.
When data collected from web content are placed in a structure, they become highly organized and easily accessible.
Search engines understand these structured data more clearly than unstructured data.
Unstructured data is data that is not neatly organized into files. It can be anything from email messages to blog posts.
Unstructured data can be difficult to work with search engines, but it can be a valuable source of information for the users.
To reach the audiences, data need to be crawled, indexed, and ranked by search engines.
Search engines need to know exactly the information on web content before ensuring its indexing and ranking.
This is why search engines like Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex encourage webmasters to apply structured data in their web content.
How Does Structured Data Work?
Google search is working hard on how to exactly understand the content of the webpage and how to present the content more visual and attractive way in search results.
Structured data is a practice of generating these organized data that help to improve this effort of Google search.
Structured data is a set of data which is marked up using a specific schema.
Schema is a language of search engines that conveys the structured data of the content and informs search engines about what the content is and how it will be visual to the users.
This schema defines the structure of the data and how it can be accessed and used.
Search engines present this marked-up data of the content in a more informative and visual way in the search result. These informative results are also known as rich results or rich snippets.
So, structured data can be used to improve the searchability and usability of web pages and applications.
It also has an impact on SEO.
This is because structured data helps search engines to know exactly what your content is and how the users can find it easily on your web page.
When Google clearly understands your content it will be easy for it to rank the content in the search result.
Also, the rich results on the search result page come out for applying structured data that are accepted by the users as more informative results than normal results.
Thus these rich results experience more CTR (Click Through Rate ) which helps in ranking.
However, this technical performance of the search result does not always mean the page is actually a better search result.
Better search results always ranked high and provide more value to the users.
These are the real purpose of applying structured data on the webpage.
What Is Structured Data and How It Works
What Is Structured Data and How It Works
How to Add Structured Data to a Web Page
We have already learned what structured data is and how it works. Now we need to know how to add it to the web page. If we can add it successfully to the web page, we can certainly see its output in the search results. In this case, of course, we have to be a little more patient. Then we don’t delay.
Let’s get started.
We need to start the following step by step.
1. Open Structured Data Markup Helper.
2. Select Data Type and Put the URL under URL Tab.
3. Select Page Elements and Allot Data Tags.
4. Click on Create the HTML Button.
5. Add the Schema Markup to Your Page
6. Test Your Markup File Using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
7. Diagnose and Fix Any Identified Issues.
1. Open Structured Data Markup Helper.
First, open the link Structured Data Markup Helper
This tool will help you to apply structure data to your content page
You can also open this link from your Google Search Console account.
2) Select the data type and put the url under the URL tab.
When you have reached Structured Data Markup Helper, follow the following steps to add markup elements to a web page.
1. Select Website tab.
2. Select a data type that you want to mark up
3. Paste the url in URL tab
4. Or, paste the HTML source of the page you wish to mark up
5. Select Start Tagging
What Is Structured Data and How It Works
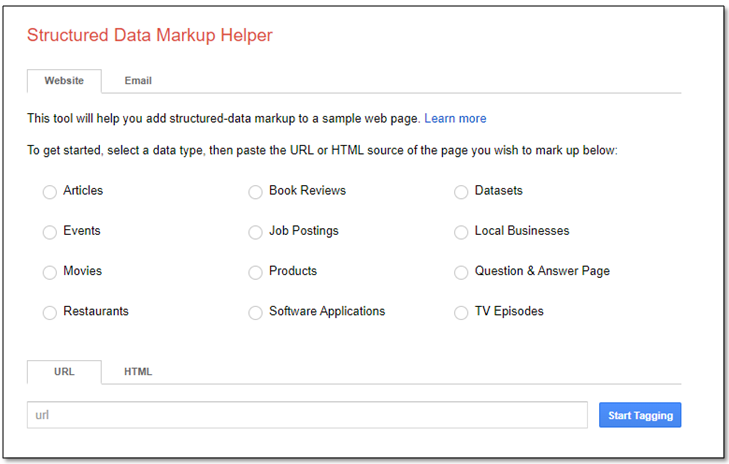
In data type, you need to select the type of the page that you want to mark up. The types are, for example, Articles, Events, Movies, Restaurants etc.
You can set multiple items on a single page. But, you are recommended to set single item since all items are of the same type.
When you enter the url of the page in the URL tab or the HTML source code of the page in the HTML tab, make sure that the page in both is available to anyone without logging in.
3) Select page elements and allot data tags.
After selecting Start Tagging, you will reach the page where on the left side you will find the URL page which you will mark up, and on the right side, you will find My Data Item where you will assign data tags.
To collect data from the page, you need to highlight or select the parts of the page that contains important information and identify the type of information.
For example, select the information like name of the page and select Name data type from the drop-down list that appears.
Thus, for an “Article” data type, you provide information like Name, Author, Date published, image, Article section, Article body, URL, Publisher, etc.
Supply all information needed for your specific data type.
If you require adding information that is not seen on your page, see Add missing data.
If you require removing a tag that Structured Data Markup Helper generated, see Remove tags.
4) Click on Create the HTML button.
As you have completed tagging all the data properly, click on Create HTML button above the My Data Items pane in the right-hand corner to generate the web page code..
You are recommended to choose the output format JSON-LD. The script as JSON-LD markup is however produced automatically by the tools. It is as default. But you can also choose the output format Microdata.
5) Add the schema markup to your page.
Now, copy and paste the code from the output window to publish the script on your webpage. For the output format JSON-LD, copy and paste the code into the body of your existing page. You can also select the Download option to get the script.
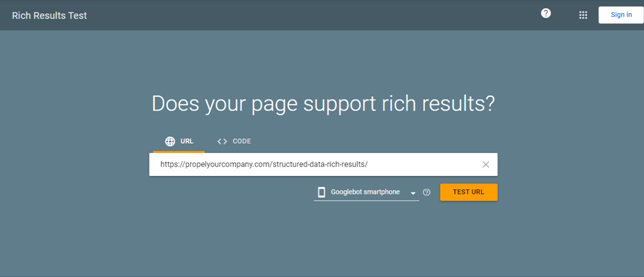
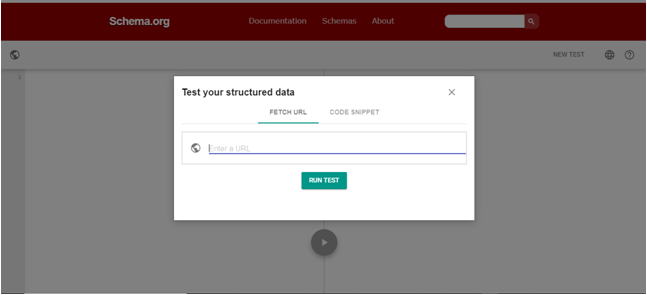
6) Test your markup file using Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
Open Rich Result Test Tools. To test the script, you need to copy the URL of your existing page where you have put the JSON-LD markup.
Paste the URL on the toolbar of the Rich Result Test Tools and press Test URL button.
It will tell you about the missing fields, that you should provide to help Google understand your page clearly.
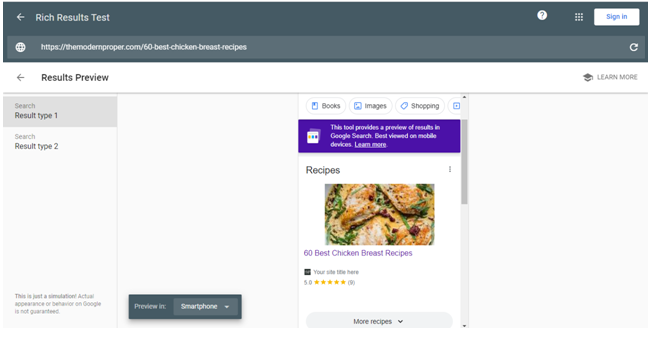
In case of some data types, it will also show you a preview of how your page might look like in Google Search Results.
Google recommends the Rich Results Test tool to see what Google-rich results can be generated for your page.
You can also put the code of JSON-LD markup on the CODE tab of Rich Results Test tool and click on Test CODE button to see the result.
Also, You can use the Schema Markup Validator to test all types of schema.org markup.
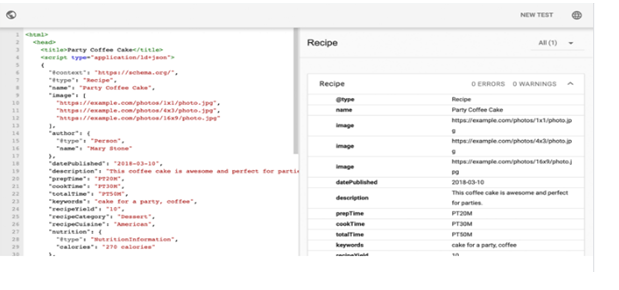
7) Diagnose and fix any detected issues.
This tool will show HTML mark up in the left side and report on the HTML Mark up in the right side you will find Errors and Warnings in red.
To fix structured data errors you can edit any errors in the HTML directly in the tool panel. Before “publishing” the tested HTML markup you should fix all the issues.
Conclusion
What Is Structured Data and How It Works
Structured data is an essential tool to provide basic information to search engines about the content for its clear understanding.
The more clearly Google understands your page data, the more attractively it will present results in Google Search.
It is an essential part of SEO for your website. This tool is easy to use and accessible to everyone. So, it can be a regular routine for SEO workers to check structured data.
Related Term:
